XL RARA BAD-5087-100-OG Clinical Applications: AMLXL RARA BA is designed as a break apart probe. The orange labeled probe hybridizes proximal to the breakpoint in the RARA gene region at 17q21, the green labeled probe hybridizes distal to the breakpoint. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is considered as a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and accounts for about 5-8% of all AML cases. Around 98% of all APL cases are characterized by the PML-RARA fusion gene. Translocations affecting RARA and other genes have been identified in only 1-2% of APL cases. RARA fusion genes interfere with myeloid differentiation and contribute in the development of APL. The majority of APL patients are responsive to therapeutic doses of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO) associated with chemotherapeutic drug regimen. The FISH break apart assay is a valuable tool for the detection of RARA rearrangements independent of the translocation partner. Download fact sheet (PDF) for further information
|
 |
XL 20q12/20qter/8cen plusD-5122-100-TC Clinical Applications: MDS, AMLThe XL 20q12/20qter/8cen plus probe detects deletions which occur in the long arm of chromosome 20. An orange labeled probe hybridizes to 20q12 to the proximal part of PTPRT and a green labeled probe hybridizes to the q-terminal region of the long arm of chromosome 20. Additionally, a blue labeled probe hybridizes to the centromere of chromosome 8. The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of hematopoietic stem cell disorders associated with ineffective hematopoiesis and peripheral blood cytopenia. MDS patients have a high risk to progress to acute leukemia. A chromosome 20q deletion is seen in about 2% of MDS cases. Patients with a sole del(20q) have a favorable outcome. About 30% of all del(20q) patients are carrying additional recurrent chromosomal abnormalities as del(5q), monosomy 7, del(7q) and trisomy 8. Download fact sheet (PDF) for further information
|
 |
XL ABL2 BAD-5138-100-OG Clinical Applications: ALLXL ABL2 BA is designed as a break apart probe. The orange labeled probe hybridizes proximal to the breakpoint in the ABL2 gene region at 1q25.2 and is covering the proximal part of ABL2, the green labeled probe hybridizes distal to the breakpoint. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a rare disease with approximately 1:100.000 new diagnoses per year. A novel high risk subtype called BCR/ABL1-like ALL or Philadelphia-like ALL was discovered based on similar gene expression profiles to BCR/ABL1-positive ALL and is characterized by aberrations, resulting in the activation of tyrosine kinase signaling pathways. Prominent genes in the JAK/STAT activating group are CRLF2, EPOR and JAK2, members of the ABL-class fusions are ABL1, ABL2, CSF1R and PDGFRB. The ABL2 gene has been initially identified as a novel fusion partner of ETV6. ABL2 belongs to the Abelson family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases and is highly similar to ABL1. Download fact sheet (PDF) for further information
|
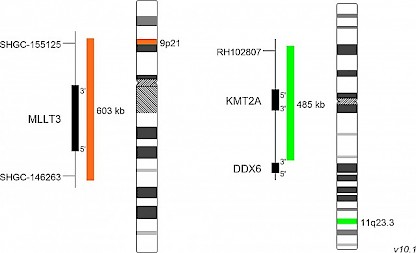
XL t(9;11) MLLT3/KMT2A DFD-5133-100-OG Clinical Applications: ALL, AMLXL t(9;11) MLLT3/KMT2A DF is designed as a dual fusion probe. The orange labeled probe spans the breakpoint at 9p21 (MLLT3), the green labeled probe spans the breakpoint at 11q23.3 (KMT2A).
The KMT2A (previous name ´MLL´) gene, located on chromosome 11q23, is rearranged in about 10% of all acute leukemia patients. Most of them suffer from acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML), only a minority shows mixed lineage leukemia which has given the gene its original name ´MLL´. Today, more than 80 translocation partners of KMT2A have been identified. KMT2A is involved in about 3-5% of adult de novo AML cases and the most common aberration in this subgroup is t(9;11)(p22;q23) involving the MLLT3 gene. Pediatric patients carrying this aberration do have a favorable outcome which is comparable to AML patients without KMT2A involvement. FISH is described as a reliable method for the identification of t(9;11).
Download fact sheet (PDF) for further information
|
 |
|