Probes Newsletter 03/2019
Newsletter 03/2019

Microdeletion Probes from MetaSystems...
Microdeletion syndromes are characterized as a heterogenous group of diseases caused by the loss of small chromosomal regions, typically 1-3 Mb in size. These genetic aberrations are not visible in classical cytogenetics. The resulting diseases occur with prevalences of up to 1:4.000 in newborns. Fluorescence in situ hybridization is one of the best-established methods to reliably detect microdeletions and confirm diagnoses of the corresponding diseases.
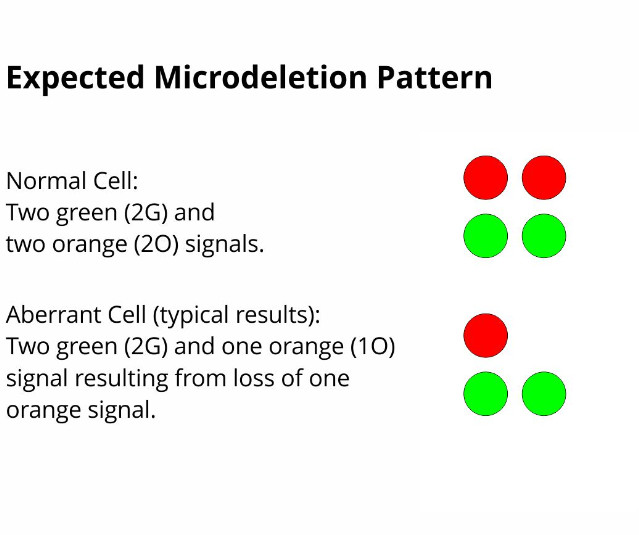
MetaSystems is further expanding its portfolio and adds several new probes for the detection of microdeletions. Today, MetaSystems launches the first three microdeletion probes covering the following syndromes: Wolf-Hirschhorn, Cri-du-Chat and Williams-Beuren. The three different microdeletion probes are packed as 50 µl units, recommended to perform 5 tests. For further information, please visit www.metasystems-probes.com

XL Wolf-Hirschhorn
Clinical Applications: Microdeletions
The association of partial 4p16 deletions with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) was first described by Cooper and Hirschhorn in 1961. Most 4p16 deletions in WHS occur de novo, only in the minority of cases the rearranged chromosome is inherited. WHS is a contiguous gene syndrome associated with haploinsufficiency of several closely linked genes. The severity of clinical manifestation depends on the amount of genetic material affected. Two WHS critical regions (WHSCR) have been identified. The classical WHSCR1, spanning 165 kb on chromosomal location 4p16.3, includes the genes NSD2 (nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 2) and NELFA (negative elongation factor complex member A). WHSCR2 was defined based on the identification of patients with atypical forms of WHS showing no deletion of WHSCR1. WHSCR2 is located distally to WHSCR1 partially including the gene NSD2, but excluding NELFA.
XL Wolf-Hirschhorn detects deletions in the short arm of chromosome 4. The orange labeled probe hybridizes to the NSD2 (WHSC1) locus at 4p16.3. The green labeled probe hybridizes to a specific locus at 4q12 and functions as a reference probe.
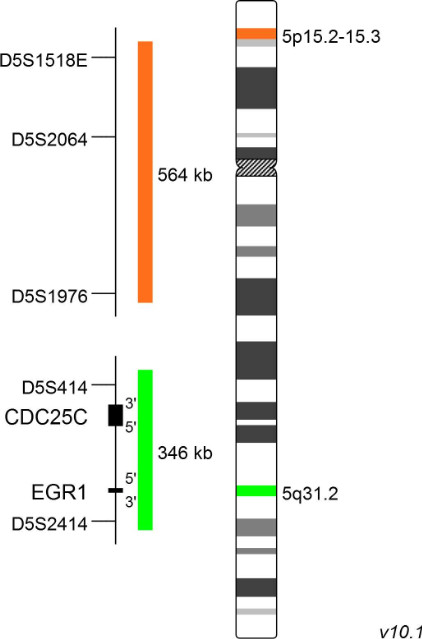
XL Cri-Du-Chat
Clinical Applications: Microdeletions
The Cri-du-Chat syndrome (CdCS), or 5p-minus syndrome, was first described by Lejeune et al. in 1963. The name refers to the main clinical feature of the syndrome, a characteristic cat-like cry in early childhood. The majority of patients carry a terminal deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5 with breakpoints ranging from 5p13 to 5p15.2 with a size of up to 40 Mb. Most 5p deletions occur de novo, probably during spermatogenesis. Breakpoints are not well defined and differ between CdCS cases. Only few patients have an interstitial deletion, translocations or other less common aberrations. Patient studies established a link between the size of the deleted region and the CdCS phenotype and identified regions 5p15.2 and 5p15.3 responsible for dysmorphism, mental retardation and the cat-like cry.
XL Cri-Du-Chat detects deletions in the short arm of chromosome 5. The orange labeled probe hybridizes to a chromosomal locus at 5p15.2-15.3. The green labeled probe hybridizes to a specific locus at 5q31.2 and functions as a reference probe.

XL Williams-Beuren
Clinical Applications: Microdeletions
The Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS) is a rare contiguous gene deletion syndrome. WBS phenotype is complex, age-dependent and varies between individuals. One of the most fatal and characteristic clinical complications is supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS). The WBS is associated with a chromosomal microdeletion in region 7q11.23. The common critical region is about 1.6 Mb in size and contains more than 20 genes, including ELN (elastin) and LIMK1 (LIM domain kinase 1). Haploinsufficiency of ELN correlates with cardiovascular problems and is responsible for the SVAS phenotype of WBS patients. Deletions in region 7q11.23 are a consequence of non-allelic homologous recombination between low copy repeat elements flanking the WBS deleted region. Most WBS cases are sporadic, only few cases are transmitted vertically.
XL Williams-Beuren detects deletions in the long arm of chromosome 7. The orange labeled probe hybridizes to the ELN locus at 7q11.23. The green labeled probe hybridizes to a specific locus at 7p11.2 and functions as a reference probe.


