XL Prader-Willi/Angelman
Deletion Probe
- Order Number
- D-5421-050-OG
- Package Size
- 50 µl (5 Tests)
- Chromosome
- 1515
- Regulatory Status
- IVDD
IVDR Certification
MetaSystems Probes has already certified a wide range of FISH probes, according to IVDR.
This product remains IVDD-certified until further notice.
Discover all IVDR-certified products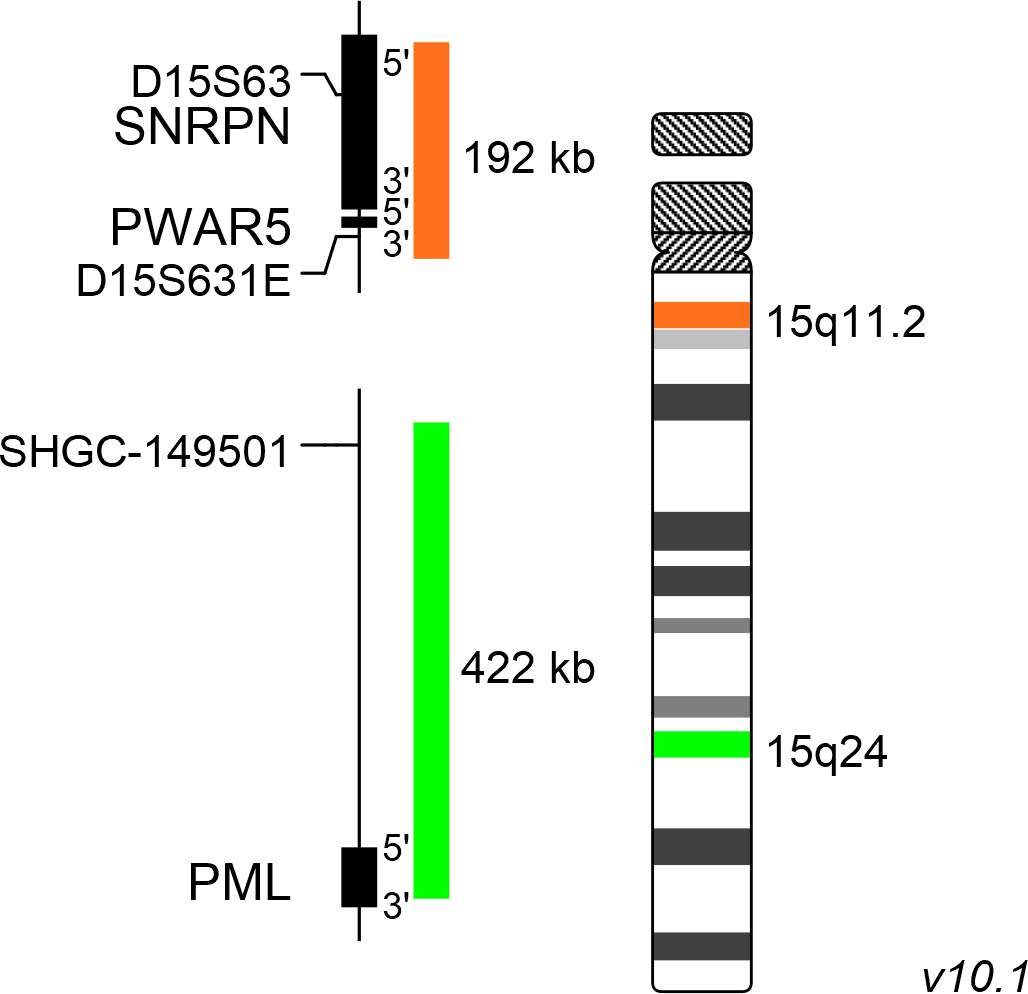
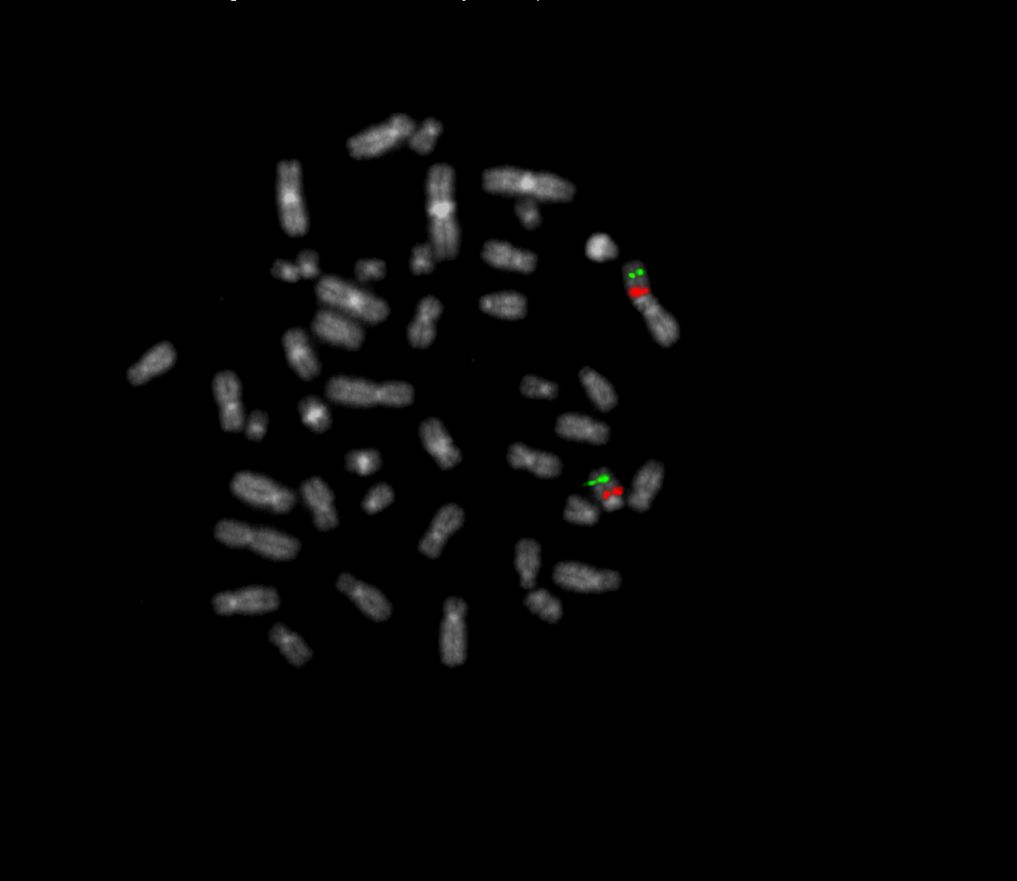
XL Prader-Willi/Angelman consists of an orange-labeled probe hybridizing to the SNRPN/PWAR5 gene region at 15q11.2 and a green-labeled probe hybridizing to the PML gene region at 15q24.
Probe maps for selected products have been updated. These updates ensure a consistent presentation of all gaps larger than 10 kb including adjustments to markers, genes, and related elements. This update does not affect the device characteristics or product composition. Please refer to the list to find out which products now include updated probe maps.
Probe map details are based on UCSC Genome Browser GRCh37/hg19, with map components not to scale.
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), first described by Prader, Labhart and Willi in 1956, and Angelman syndrome (AS) initially reported by Angelman in 1963, are complex neurodevelopmental disorders caused by chromosomal deletion of genes in the 15q11-q13 region. In most cases, the corresponding genes are silenced on the sister chromosome via genetic imprinting. The deletion of the paternal segment 15q11-q13 leads to the development of PWS, while patients carrying the maternal deletion of this segment suffer from AS. The clinical manifestation of PWS is characterized by muscular hypotony (´floppy infants´), hypogonadism, developmental and cognitive delays, hyperphagia and obesity. Furthermore, learning disabilities and obsessive-compulsive disorder can be observed. Typical AS indications observed are a small head, severe intellectual disability and developmental retardation. Speaking, sleep, balance and movement problems, as well as seizure disorder are further symptoms. The most common genetic cause for PWS is the deletion of the paternal 15q11-q13 copy. Maternal uniparental disomy of 15q11-q13 (genes are silenced via genetic imprinting) or translocations with breaks in the 15q11-q13 region are further mechanisms leading to PWS. Genes located in this region, especially SNRPN (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N) and NDN (necdin), are considered to be crucial for disease development. The absence of the maternal UBE3A (ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A) gene copy located in this segment is crucial for the development of AS.
Clinical Applications
- Microdeletion Syndrome (MicroDel)

Normal Signal Pattern:
Two green (2G) and two orange (2O) signals.

Aberrant Signal Pattern:
Two green (2G) and one orange (1O) signal resulting from loss of one orange signal.
- Clayton-Smith and Pembrey (1992) Med Genet 29:412-415
- Butler (2011) Curr Genomics 12(3):204-215
- Kalsner and Chamberlain (2015) Pediatr Clin North Am 62(3):587-606
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
or go to CoA Database