XL t(14;18) IGH/MALT1 DF
Translocation/Dual Fusion Probe
- Order Number
- D-6020-100-OG
- Package Size
- 100 µl (10 Tests)
- Regulatory Status
- IVDD
IVDR Certification
MetaSystems Probes has already certified a wide range of FISH probes, according to IVDR.
This product remains IVDD-certified until further notice.
Discover all IVDR-certified products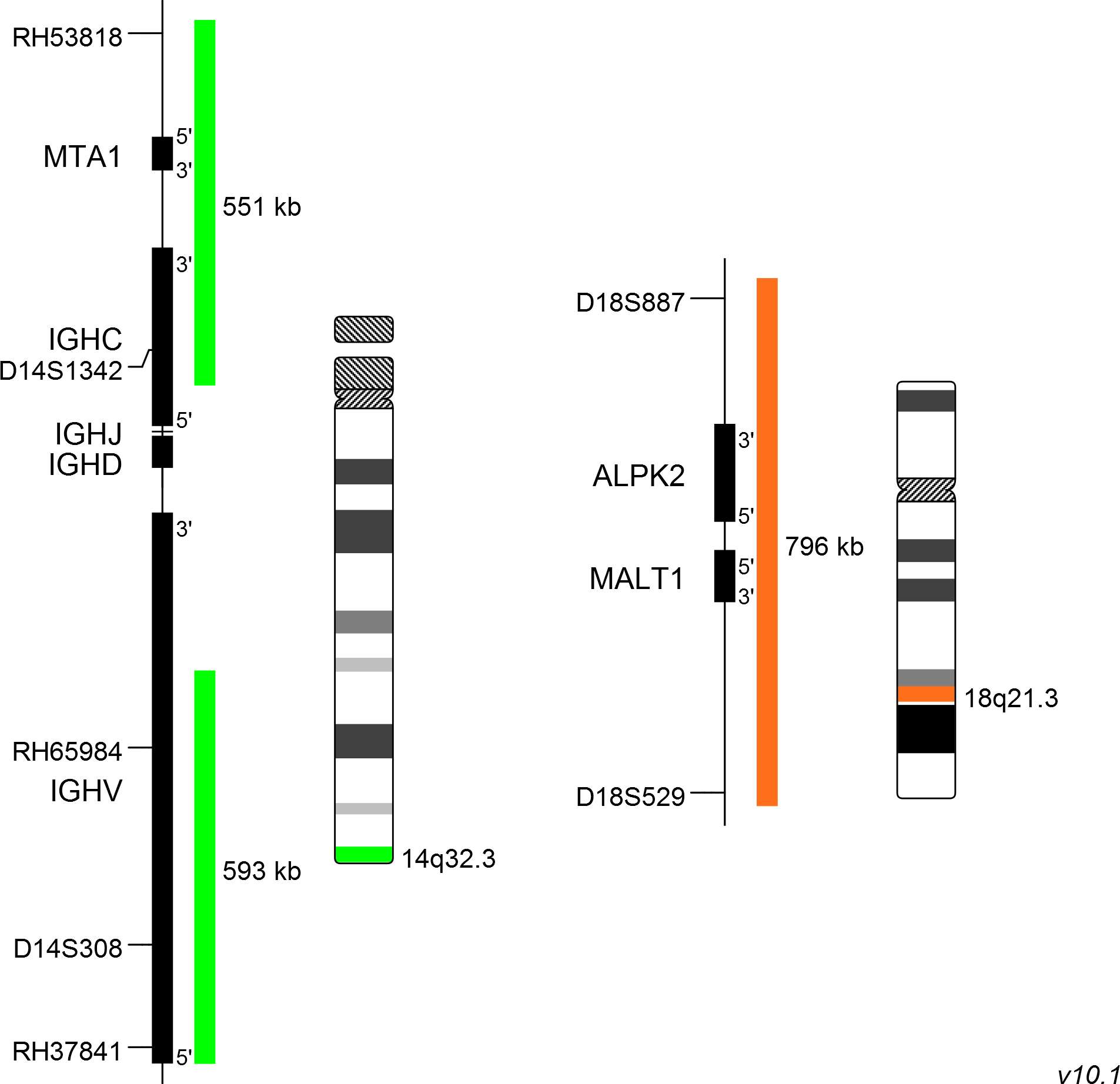
XL t(14;18) IGH/MALT1 DF consists of a green-labeled probe hybridizing to the IGH gene region at 14q32.3 and an orange-labeled probe hybridizing to the MALT1 gene region at 18q21.3.
Probe maps for selected products have been updated. These updates ensure a consistent presentation of all gaps larger than 10 kb including adjustments to markers, genes, and related elements. This update does not affect the device characteristics or product composition. Please refer to the list to find out which products now include updated probe maps.
Probe map details are based on UCSC Genome Browser GRCh37/hg19, with map components not to scale.
MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) lymphomas occur at diverse anatomic sites and are closely linked to several distinct chronic inflammatory disorders. Up to 50% of the MALT lymphoma cases analyzed demonstrate MALT1 rearrangements. The MALT1 gene was originally identified by its involvement in the MALT lymphoma associated translocation t(11;18)(q21;q21). This rearrangement is detected in 30% of all cases of MALT lymphoma and leads to BIRC3-MALT1 fusions. It is restricted to MALT lymphomas and has not been detected in nodal or splenic marginal zone lymphomas, diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, or other non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
Approximately 20% of MALT lymphoma cases analyzed are characterized by t(14;18)(q32;q21) leading to a IGH-MALT1 fusion. This reciprocal translocation juxtaposes MALT1 to transcriptional enhancers in the IGH locus and results in overexpression of the MALT1 gene. The distinct breakpoints on both chromosomes are precisely defined. The oncogenic potential of MALT1 is linked to its participation in the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). This important transcription factor mediates the expression of anti-apoptotic, cell survival- and proliferation-promoting genes. Furthermore, there is emerging evidence indicating an oncogenic cross-link between the above-mentioned genetic rearrangements and immunological stimulation occurring during the pathogenesis of MALT lymphoma.
Clinical Applications
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (NHL)

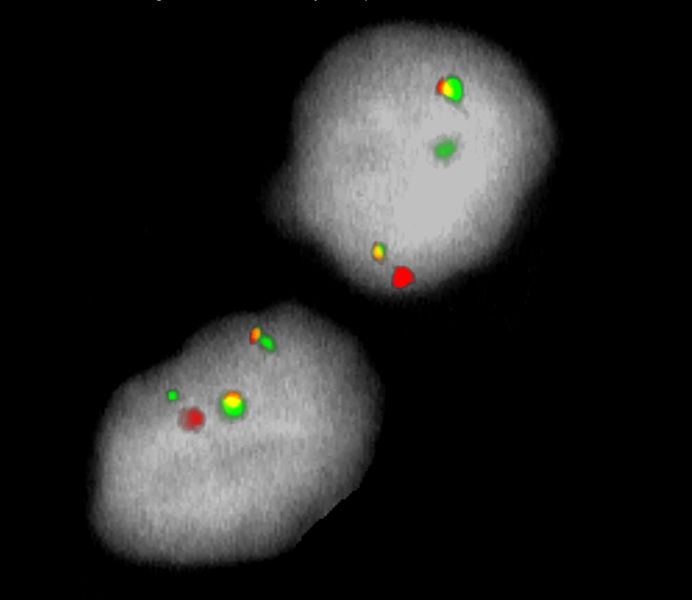
Normal Cell:
Two green (2G) and two orange (2O) signals.

Aberrant Cell (typical results):
One green (1G), one orange (1O), and two green-orange colocalization/fusion signals (2GO) resulting from a reciprocal translocation between the relevant loci.
- Streubel et al (2003) Blood 101:2335-2339
- Bacon et al (2007) J Clin Pathol 60:361-372
- Du (2017) Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 30:13-23
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
or go to CoA Database