XL IRF4 BA
Break Apart Probe
- Order Number
- D-6040-100-OG
- Package Size
- 100 µl (10 Tests)
- Chromosome
- 066
- Regulatory Status
- IVDD
IVDR Certification
MetaSystems Probes has already certified a wide range of FISH probes, according to IVDR.
This product remains IVDD-certified until further notice.
Discover all IVDR-certified products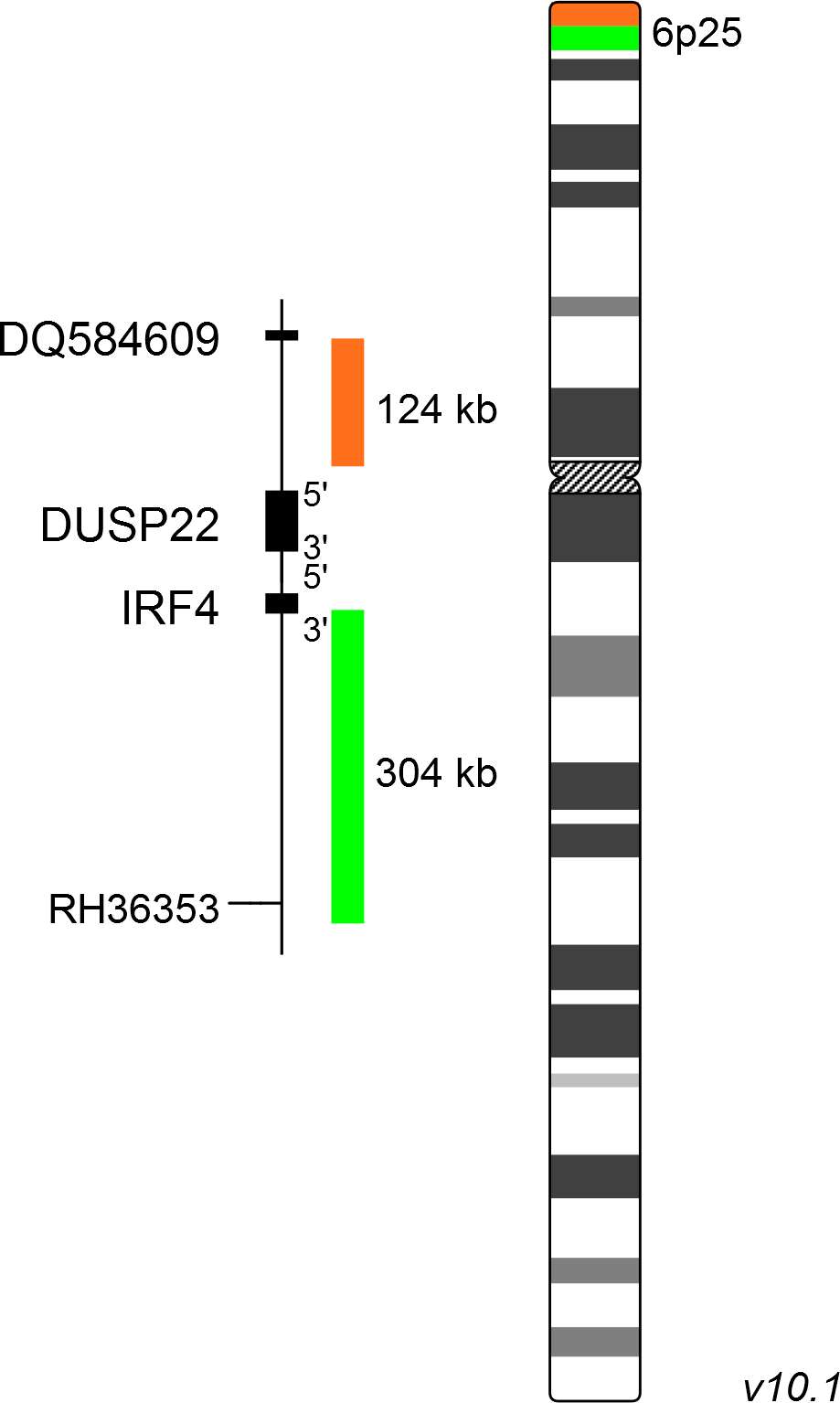
XL IRF4 BA consists of a green-labeled probe hybridizing proximal to the IRF4 gene region at 6p25 and an orange-labeled probe hybridizing distal to the IRF4 gene region at 6p25.
Probe maps for selected products have been updated. These updates ensure a consistent presentation of all gaps larger than 10 kb including adjustments to markers, genes, and related elements. This update does not affect the device characteristics or product composition. Please refer to the list to find out which products now include updated probe maps.
Probe map details are based on UCSC Genome Browser GRCh37/hg19, with map components not to scale.
The updated (2016) revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumors of lymphoid neoplasms considers the large B-cell lymphoma with IRF4 rearrangement as a new provisional entity. Head and neck regions including the Waldeyer ring are particularly affected. Chromosomal translocations involving the IRF4 gene and the immunoglobulin loci IGH, IGL and IGK (IG) result in dysregulation of IRF4 expression; other translocation partners may occur. Since t(6;14)(p25;q32) is cytogenetically cryptic, FISH is a valuable tool in detecting this recurrent aberration. IG/IRF4 positive lymphomas normally lack t(14;18), which is observed in about 85% of adult patients with follicular lymphoma, and are commonly associated with young age and a good course. IRF4 rearrangements have also been identified in peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCL). PTCL are defined as a diverse group of aggressive lymphomas of mature-stage T-cells accounting for about 10% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Recent data suggests that IRF4 translocations detected by FISH have a predictive value for primary cutaneous CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
Clinical Applications
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (NHL)

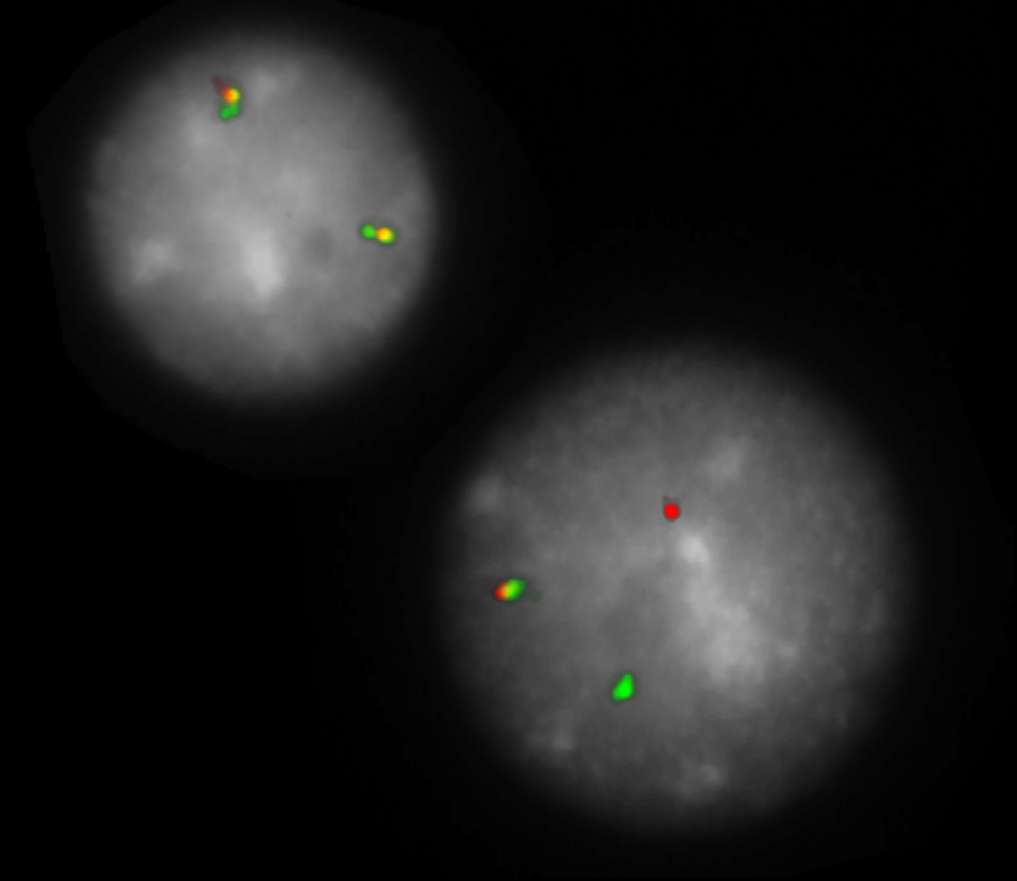
Normal Cell:
Two green-orange colocalization/fusion signals (2GO).

Aberrant Cell (typical results):
One green-orange colocalization/fusion signal (1GO), one separate green (1G) and orange (1O) signal each resulting from a chromosome break in the respective locus.
- Feldman et al (2009) Leukemia 23:574-580
- Salaverria et al (2011) Blood 7:139-147
- Kiran et al (2013) Leukemia Research 37:396-400
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
or go to CoA Database