XL TLX3 BA
Break Apart Probe
- Order Number
- D-5129-100-OG
- Package Size
- 100 µl (10 Tests)
- Chromosome
- 055
- Regulatory Status
- IVDD
IVDR Certification
MetaSystems Probes has already certified a wide range of FISH probes, according to IVDR.
This product remains IVDD-certified until further notice.
Discover all IVDR-certified products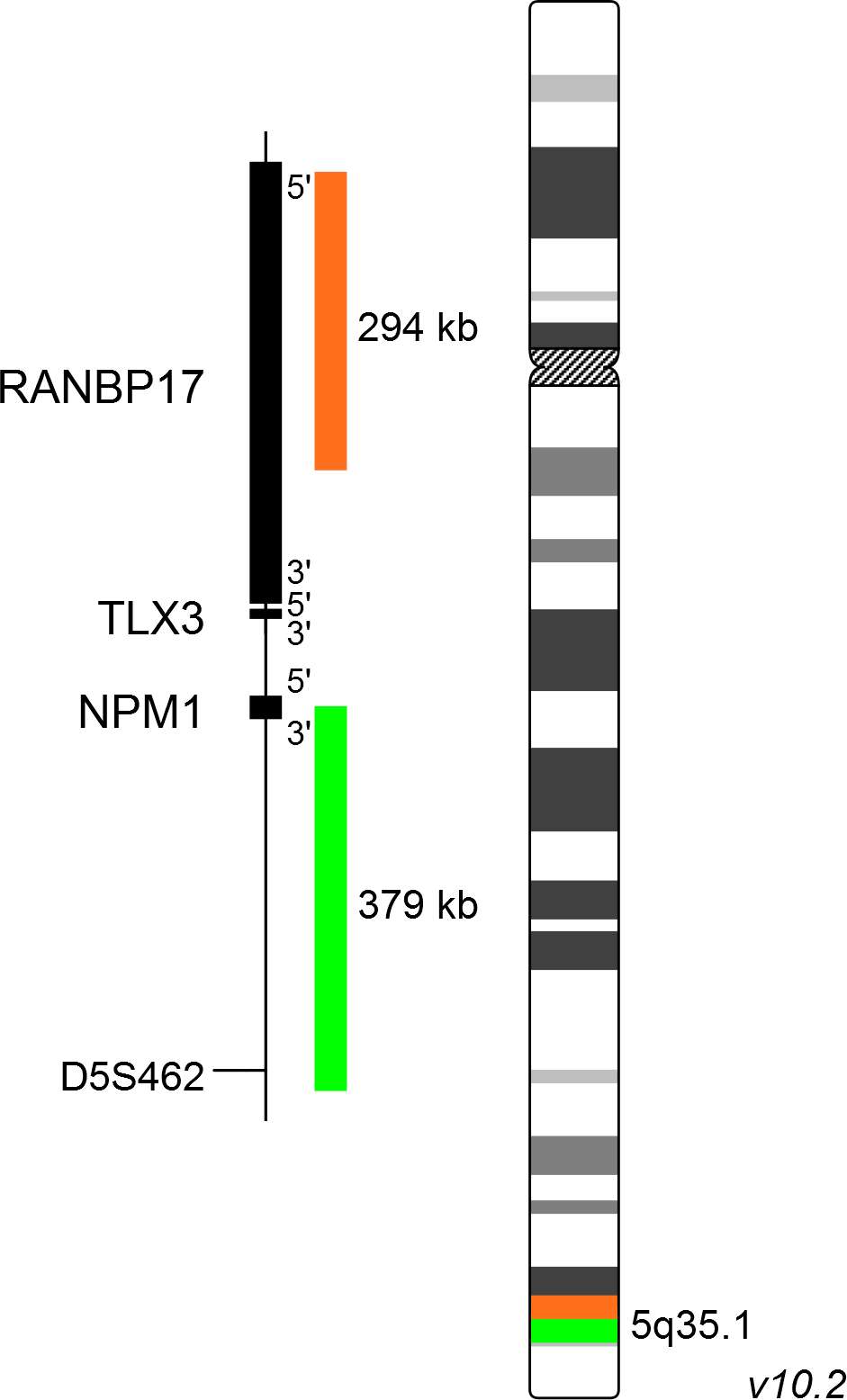
XL TLX3 BA consists of an orange-labeled probe hybridizing proximal to the TLX3 gene region at 5q35.1 and a green-labeled probe hybridizing distal to the TLX3 gene region at 5q35.1.
Probe maps for selected products have been updated. These updates ensure a consistent presentation of all gaps larger than 10 kb including adjustments to markers, genes, and related elements. This update does not affect the device characteristics or product composition. Please refer to the list to find out which products now include updated probe maps.
Probe map details are based on UCSC Genome Browser GRCh37/hg19, with map components not to scale.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common childhood cancer type. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive and quickly progressing type of ALL affecting T-lymphocytes. Genomic data suggests that more than 10 functional aberrations are contributing to the development of this disease. T-ALL cases can be grouped by distinct genetic profiles and the aberrant expression of a characteristic transcription factor. Major subgroups are characterized by ectopic expression of TAL1, TLX1, TLX3, HOXA9/10, LMO2 or NKX2-1 and others as a result of chromosomal rearrangements or mutations. About 20% of childhood T-ALL cases are characterized by aberrant expression of TLX3 as a result of t(5;14)(q35;q32). This cryptic translocation juxtaposes TLX3, normally not expressed in T-cells, with the BCL11B gene, which is active in T-cells, resulting in ectopic expression of TLX3.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization is a valuable method for the detection of t(5;14)(q35;q32) since cryptic translocations may escape during classical cytogenetic analysis. Furthermore, the broad range of breakpoints in the chromosomal region 14q32 makes the development of efficient PCR-based methods difficult.
Clinical Applications
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)

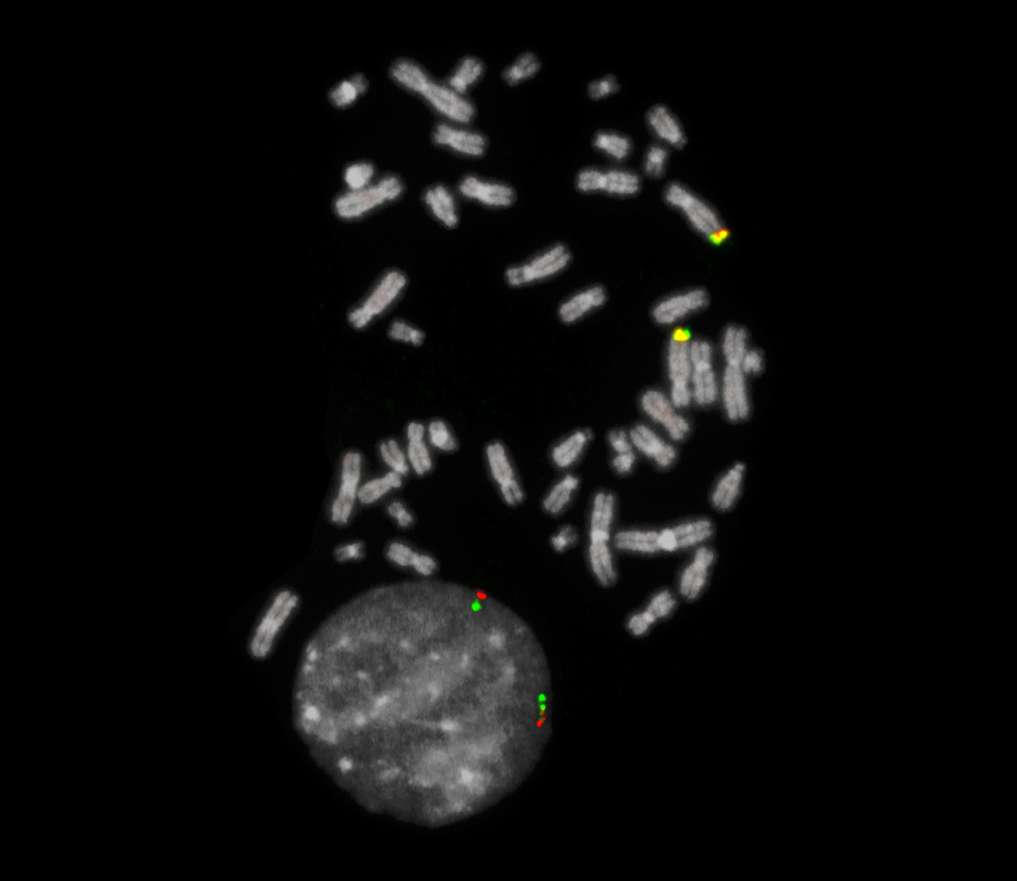
Normal Cell:
Two green-orange colocalization/fusion signals (2GO).

Aberrant Cell (typical results):
One green-orange colocalization/fusion signal (1GO), one separate green (1G) and orange (1O) signal each resulting from a chromosome break in the relevant locus.
- Van Zutven et al (2004) Haematologica 89:671-678
- Su et al (2006) Blood 108:4198-4201
- Girardi et al (2017) Blood 129:1113-1123
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
or go to CoA Database