XL FOXO1 BA
Break Apart Probe
- Order Number
- D-6034-100-OG
- Package Size
- 100 µl (10 Tests)
- Chromosome
- 1313
- Regulatory Status
- IVDD
IVDR Certification
MetaSystems Probes has already certified a wide range of FISH probes, according to IVDR.
This product remains IVDD-certified until further notice.
Discover all IVDR-certified products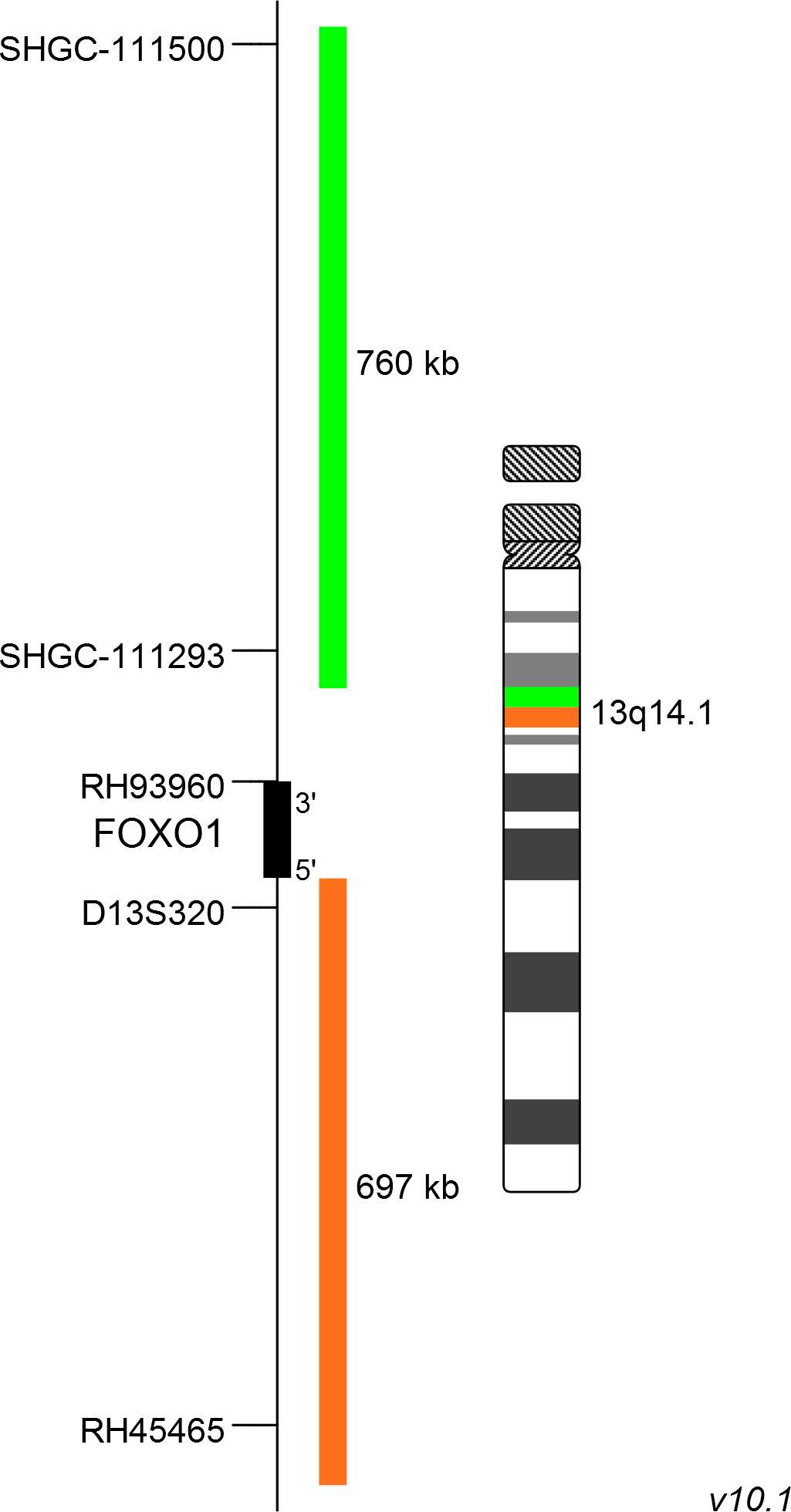
XL FOXO1 BA consists of a green-labeled probe hybridizing proximal to the FOXO1 gene region at 13q14.1 and an orange-labeled probe hybridizing distal to the FOXO1 gene region at 13q14.1.
Probe maps for selected products have been updated. These updates ensure a consistent presentation of all gaps larger than 10 kb including adjustments to markers, genes, and related elements. This update does not affect the device characteristics or product composition. Please refer to the list to find out which products now include updated probe maps.
Probe map details are based on UCSC Genome Browser GRCh37/hg19, with map components not to scale.
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a relatively rare cancer type but it is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children and adolescents. The histopathological classification includes several subtypes: embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) are the most common variants, in the order of their occurrence. ARMS is associated with a worse outcome and is characterized by the two reciprocal translocations t(2;13)(q35;q14) and t(1;13) (p36;q14), affecting the FOXO1 gene region and PAX3 or PAX7 respectively, in about 80% of cases. The result is an in-frame fusion of the PAX DNA binding domain with the transcriptional active domain of FOXO1 generating a highly potent chimeric activator for PAX target genes. Patients harboring FOXO1-PAX3/7 fusions have an inferior event-free survival compared to patients without translocation, suggesting that the molecular status in RMS provides valuable prognostic information.
Clinical Applications
- Solid Tumors (Solid Tumors)

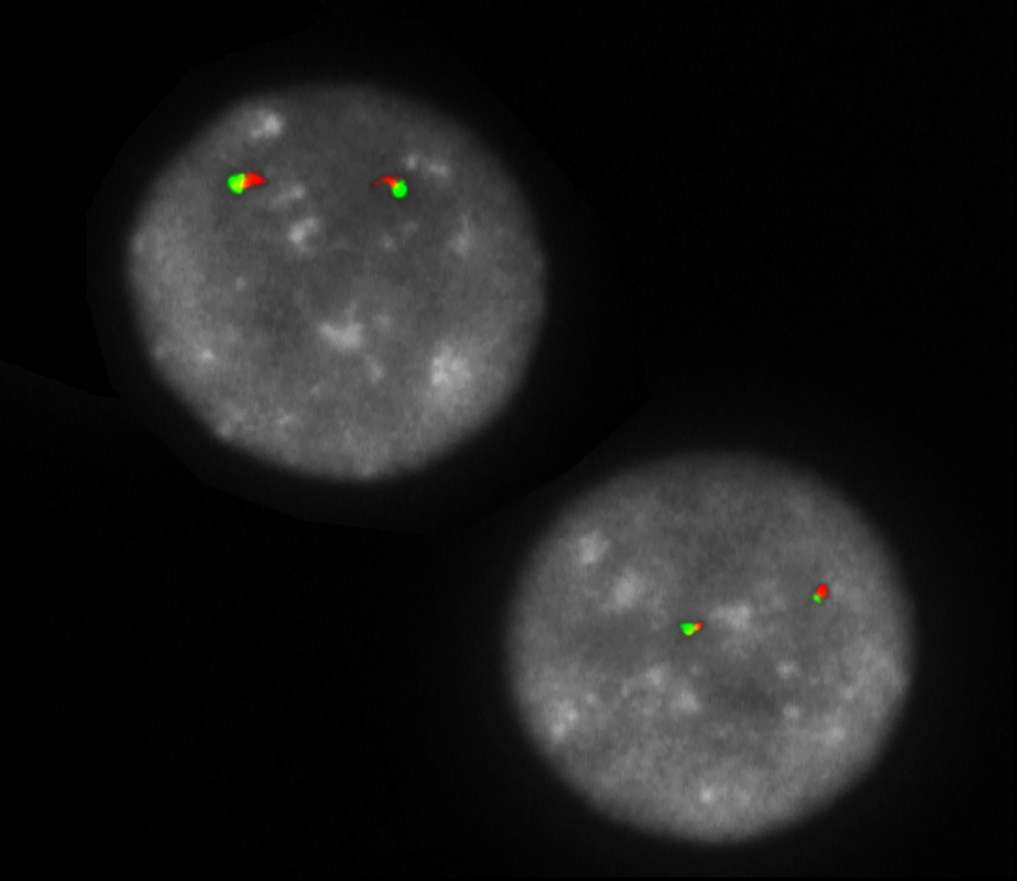
Normal Cell:
Two green-orange colocalization/fusion signals (2GO).

Aberrant Cell (typical results):
One green-orange colocalization/fusion signal (1GO), one separate green (1G) and orange (1O) signal each resulting from a chromosome break in the relevant locus.
- McManus et al (1996) J Pathol 178:410–414
- Barr (2001) Oncogene 20:5736-5746
- Skapek et al (2013) Pediatr Blood Cancer 60:1411-1417
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
or go to CoA Database